Reaching to get an item from a shelf, combing your hair, and putting on a sweater are activities that many people take for granted, but they can become difficult or impossible if you suffer from a torn rotator cuff. While some rotator cuff injuries heal with minimal treatment, accident victims with significant tears often need one or more surgeries. The pain from your injury and the expense of ongoing treatment can disrupt your personal relationships, hobbies, and work.
What Is a Torn Rotator Cuff?
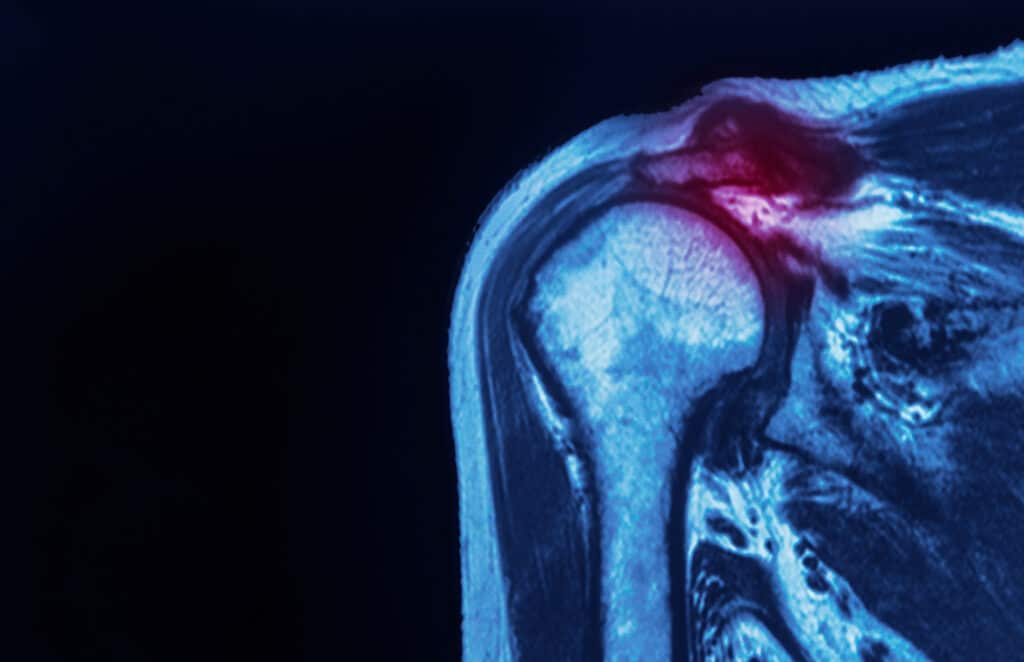
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that surround your shoulder joint. They keep your upper arm bone in your shoulder socket and attach it to your shoulder blade, allowing you to lift and stretch your arms upward. If the tendon in the rotator cuff tears, it can cause intense pain and make it difficult to move your arms normally. According to Cedars Sinai, rotator cuff injuries are common, with millions of Americans seeking treatment for them each year.
Causes
Some rotator cuff tears develop over time as a result of tissue degeneration. Others, known as acute tears, occur due to trauma. Situations that can lead to this type of injury include:
- Car accidents. Rotator cuffs can tear during car accidents if you tighten your shoulders at the moment of impact.
- Falls. Tears are often the result of a slip-and-fall accident, particularly if you land on your outstretched hand.
- Repetitive motion. Painters and other professionals who frequently lift their arms may gradually develop a rotator cuff tear.
Accident victims with torn rotator cuffs often have other injuries, such as dislocated shoulders or broken collarbones, which can complicate the treatment and recovery process.
Types
When medical professionals treat torn rotator cuffs, they usually categorize them as partial or full-thickness tears. If you have a partial tear, it doesn’t go completely through the tendon and is still attached to the bone. Partial tears are primarily the result of degeneration or repetitive motion. Accident victims are more likely to develop full-thickness tears. These injuries are more difficult to treat and may require surgery because part or all of the tendon is detached from the bone.
Symptoms of Rotator Cuff Tears
The most prevalent symptom of a rotator cuff tear is pain, but the severity depends on the extent and type of the tear. The discomfort is often worse at night or when moving the shoulder into certain positions. People with rotator cuff injuries may also experience weakness in the affected shoulder and arm and a crackling sensation known as crepitus when moving.
Doctors diagnose tears by evaluating a patient’s symptoms and discussing any recent incidents that could have caused an injury. They also use imaging tests, including MRIs and X-rays, to examine the internal components of the shoulder, determine whether a tear exists, and evaluate how serious it is.
Treatment for Rotator Cuff Injuries
The strategy to address a torn rotator cuff differs based on the size, location, and depth of the tear. Many patients experience a full recovery with nonsurgical treatment options, such as:
- Rest and activity modification. Limiting the use of the shoulder may help it to heal naturally.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. Over-the-counter pain medication can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Physical therapy. Physical therapists use stretches and exercises to improve shoulder flexibility and strength.
- Steroid injections. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons reports that steroid shots provide two-thirds of rotator cuff patients with pain relief for a period of three months or more.
Unfortunately, nonsurgical treatments aren’t successful for everyone. The tear may increase in size over time and pain may worsen. In those cases or when a rotator cuff suddenly tears during an accident, surgery is usually necessary.
Risks From a Torn Rotator Cuff
A rotator cuff tear can affect your short and long-term health and quality of life. Many people with these injuries have a hard time sleeping because they can’t find a comfortable position and their pain increases at night. A shoulder injury can also interfere with your ability to take care of yourself and carry out everyday activities, such as getting dressed or washing and brushing your hair.
If you have a rotator cuff injury and don’t receive proper treatment, you might permanently lose the range of motion and strength in your shoulder joint. Even patients who undergo surgery can experience complications, including nerve injuries, infections, and stiffness. Severe tears sometimes re-tear after the initial recovery and require additional surgeries. When the repair is unsuccessful or if the tendon tears again, doctors resort to more complex procedures, such as tendon transfers or complete shoulder-joint replacements.
Damages for Torn Rotator Cuff Injuries
Victims of rotator cuff injuries can seek compensation if their accident was the result of someone else’s negligent or reckless behavior. For instance, if a distracted driver rear-ends your car, they may be liable for damages, such as:
- Medical bills. The costs to treat a rotator cuff include bills for surgery, physical therapy, medication, ultrasound treatments, and imaging tests. According to a 2022 study, surgery for a full-thickness tear costs $34,249, on average.
- Lost wages or earning capacity. People with rotator cuff tears often have to take time off work to rest, prepare for surgery, and recover from their operation. They may also have a reduced earning capacity in subsequent years because of limitations on their range of motion.
- Pain and suffering. Suffering from a torn rotator cuff can be physically and emotionally painful and draining. Changes in a victim’s social and professional life can cause depression and anxiety.
The total damages in a personal injury case should include past and future expenses related to your torn rotator cuff. For example, in addition to covering your past medical costs, your settlement should also account for treatment, pain medication, and surgeries that doctors believe might be necessary in the months and years to come.
SOURCES:
1. Rotator Cuff Injury. Johns Hopkins Medicine. Accessed October 26, 2023.
2. Rotator Cuff Injury. Cedars Sinai. Accessed October 26, 2023.
3. What to Know About Crepitus in Your Shoulders. WebMD. Accessed October 26, 2023.
4. Tendon transfer to repair rotator cuff. Mayo Clinic. Accessed October 26, 2023.
5. Shoulder Replacement. Cleveland Clinic. Accessed October 26, 2023.
6. Rotator Cuff Tears. OrthoInfo. Accessed October 26, 2023.
7. Direct and indirect economic burden associated with rotator cuff tears and repairs in the US. National Library of Medicine. Accessed October 26, 2023.