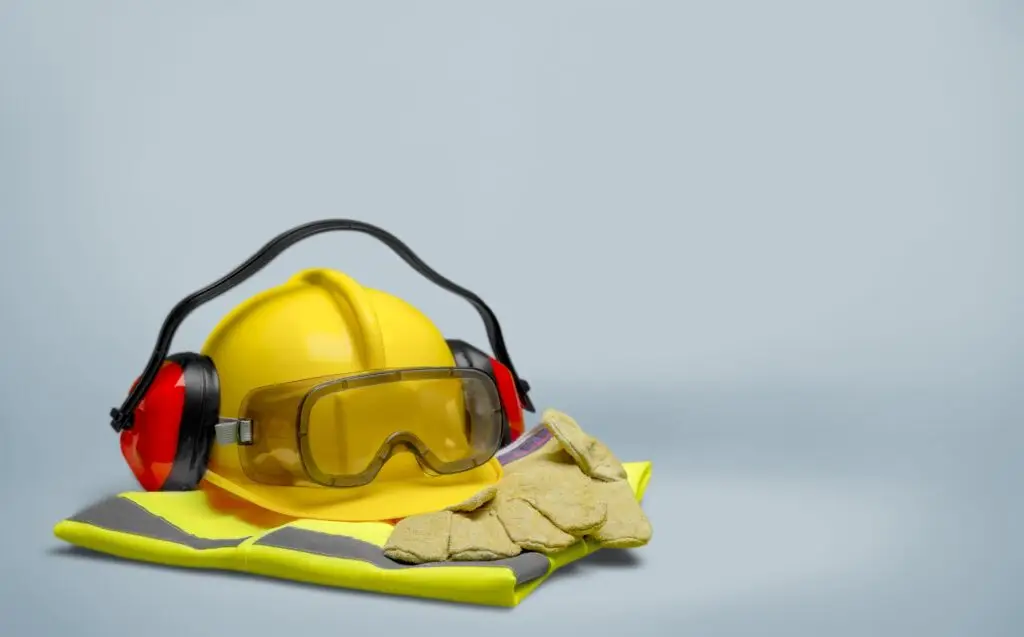
Workplaces can be dangerous. Employees could work in a factory with heavy machinery or on an oilfield or offshore rig. Construction workers use dangerous tools and climb to high heights. These workplace dangers can lead to serious injuries if employees do not have the safety equipment they need.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) can save employees from injuries and death. Many workplaces provide PPE, but some do not — even if they are required to do so. Understanding what PPE is and why it is used can help an employee stay safe on the job.
Types of Personal Protective Equipment in the Workplace
Staying safe at work is critical for any employee’s health. Employers are responsible for focusing on worker safety and providing the necessary PPE to accomplish that goal. In 2020, the term “PPE” suddenly entered the public vernacular due to the COVID-19 pandemic. To most, PPE means masks, latex gloves, and other devices meant to stop the transmission of germs.1
While this type of PPE is important, many others exist to protect Texas and Louisiana workers. Types of protective equipment include:
Head Protection
Helmets, hats, and other protective headgear help keep employees safe. They protect against falling heavy objects and impacts from large machines. Head protection is typically necessary on industrial sites and in the manufacturing industry. Head protection may help stop:
- Traumatic brain injuries
- Head cuts
- Penetrating injuries
- Facial scarring and disfigurement
Face and Eye Protection
Many jobs create risks to an employee’s eyesight. Harm may include eyeball scratches, conjunctivitis, burns, and corneal abrasions. Serious injuries could even result in blindness or the loss of an eye. Eye protection is critical for industrial workers exposed to hazards such as:
- Dangerous chemicals that could splash
- Ultraviolet light or radiant energy from welding or soldering
- Dangerous particular matter in the air
- Shrapnel or sawdust
- High heat sources
Face and eye protection usually includes safety glasses, goggles, or face masks. The type of PPE required will depend on the employee’s particular job duties.
Hearing Protection
Some workers are frequently exposed to loud noises that can damage their hearing. This damage can happen slowly over time, such as in a loud factory. Other incidents, such as a large oil refinery explosion, can cause instant damage or deafness.
Hearing protection can help prevent much of this damage. PPE may include ear plugs, ear muffs, or distancing employees from loud machinery as much as possible.
Protective Gloves
Jobs put some workers’ hands in harm’s way. Protective gloves can alleviate many of these risks. Gloves help prevent amputation, cuts, fractures, and burns. They also protect sensitive skin from harsh working conditions, such as in construction.
Gloves should fit properly and be appropriate for the hazard. For example, vinyl or latex gloves used to protect against disease are not appropriate for protecting against sharp objects in a plant. Garden gloves are insufficient to protect a welder from the high heat of the torch. Employers are expected to provide the proper hand protection in many industries.
Bodily Injury Protection
Other PPE is meant to cover parts of the body or all of it to protect against harm. This guards against dangers such as radiation, chemical exposure, high heat, and cuts. Body PPE might include:
- Protective vests
- Reflective clothing
- Shin guards
- Long sleeves
- Cut-resistant clothing
- Full-body suits
Full-body PPE is especially important for those working in dangerous medical conditions or those around radioactive materials. This equipment requires intensive training and experience to use properly.
Protective Boots and Footwear
Many workplaces require a lot of walking or pose risks to workers’ feet. For example, oil and gas workers often need anti-slip boots for working around slick surfaces. Industrial workers need steel-toed and penetration-resistant footwear to avoid severe foot damage.
Additional protective footwear may include:
- Knee pads
- Protective socks
- Shin and ankle guards
- Insoles and shoe inserts
- Electrically conductive boots
- Leggings
- Toe guards
- Metatarsal guards
Protection From Slips and Falls
Slip and fall accidents are exceedingly common in the workplace. PPE plays a vital role in limiting and preventing these accidents.2 Slip-proof footwear provides traction in otherwise slippery areas. Safety harnesses and lanyards help prevent falls from a great height, many of which would otherwise prove fatal.
Why Is PPE Used?
PPE is used for two primary reasons:
Protecting the Health and Safety of Workers
The first and most important reason to use PPE is to protect people. Workers exposed to dangerous working conditions deserve as much protection as possible. For example, the construction industry has a high prevalence of accidents and injuries. Many of these injuries are due to inadequate risk management measures, according to one study.3 The study showed that PPE utilization is often low, directly correlating with higher incidents of catastrophic injury.
PPE helps to prevent serious harm such as:
- Blindness
- Deafness
- Severe burns
- Blunt force trauma
- Amputation
- Broken bones and fractures
- Electrocution
- Spinal cord injuries and paralysis
- Wrongful death
Federal and State Requirements for Employers
Both state and federal laws require PPE for certain jobs. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) mandates that employers provide equipment based on the hazards their employees face. These regulations even dictate how to care for the equipment, who should purchase the PPE, and how to select appropriate safety devices.4 OSHA also imposes workplace safety standards that include PPE.5
Employers who willfully or repeatedly violate PPE requirements could face stiff penalties from OSHA. Companies could face a civil penalty of $5,000 to $70,000 for each willful violation. These fines can quickly accumulate, and many employers comply with the law to avoid these risks. Many state laws act similarly and require safety equipment for dangerous jobs.
PPE Is Important for Worker Safety
Employees deserve the protective equipment they need to work safely, and employers are responsible for providing it. When they do not, employers could face governmental fines and be financially responsible through a personal injury claim. An injured worker may be owed substantial compensation for their injuries.
Sources:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). Personal Protective Equipment.
- U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Fall Protection.
- National Library of Medicine, National Center for Biotechnology Information. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Use and Its Relation to Accidents Among Construction Workers.
- U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Safety and Health Administration. 1910.13(A) General Requirements.
- U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Personal Protective Equipment, Standards.
- U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Sec. 17. Penalties.